types of analyzers in laboratory|ARCHITECT c4000 Clinical Chemistry : tv shopping There are three different interface types for laboratory analyzers: network-based, serial-based, and file-based. Network-based interfaces are the most common type used in modern clinical laboratories. These interfaces use . webPlay Hellboy slots at this warm sunny casino and enjoy an amazing $2500 free money .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Tenis de mesa. 4. Destacados Competiciones. Internacionales - TT Cup. 2. República Checa - TT Star Series. 1. TT Elite Series - Masculino. 1.
Types of clinical laboratory analyzers
With the broad range of analyzers available, lab leaders must carefully weigh their options and select the right technology that meets their lab’s needs today and supports future testing volumes and growth.The history of discrete sample analysis for the clinical laboratory began with the introduction of the "Robot Chemist" invented by Hans Baruch and introduced commercially in 1959 [1]. The AutoAnalyzer is an early example of an automated chemistry analyzer using a special flow technique named "continuous flow analysis (CFA)", invented in 1957 by .Because analytical lab instruments vary in available analysis, it is important to identify key information that must be obtained from your lab analysis. Once you have identified the appropriate type of instrument for your analytical needs, the following factors are key considerations as you evaluate various offerings from available .
There are three different interface types for laboratory analyzers: network-based, serial-based, and file-based. Network-based interfaces are the most common type used in modern clinical laboratories. These interfaces use . Lab analysts: Scientists or researchers who perform tests on collected data; The lab tests may include chemical identification, object identification, DNA analysis, fingerprint analysis, document analysis, trace analysis of fibers and hair, or explosive investigations. One of the most advanced forensic labs across the world is at the FBI .
why does tip come off moisture meter for gardens
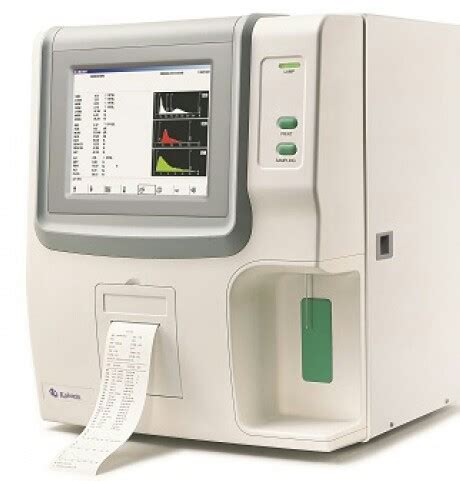
Hematology Analyzer Types by Automation Level 1. Manual Hematology Analyzers: Description: These are the most basic type, requiring significant manual intervention by lab technicians. They involve tasks like preparing blood smears, manually counting cells under a microscope, and performing calculations to derive results.The advantage of in-situ analyzers over traditional laboratory analysis is that they can provide real-time or near real-time results and do not require the sample to be removed from its environment. TDL Analyzers (Tunable Diode Laser Analyzers) TDL (Tunable Diode Laser) Analyzer is a type of gas analyzer that uses a laser beam to measure the .
Types of Analytical Laboratory Services . By testing process: Assays/Quantitative: An assay or quantitative analysis determines the amount or percentage of one or more constituents or components of a sample. Deformulation/Reverse Engineering: Deformulation uses analytical procedures to identify a chemical substance's composition. Reverse . This type of rapid analysis allows for any non-conforming results to initiate a more detailed analysis by an appropriate laboratory for verification and interpretation. The development of such devices is causing a seismic shift in the analytical landscape and could bring testing in-house, as in the case with ATP (adenosine triphosphate .The Schuster Laboratory, University of Manchester (a physics laboratory). A laboratory (UK: / l ə ˈ b ɒr ə t ər i /; US: / ˈ l æ b r ə t ɔːr i /; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratories are found in a variety of settings such as schools, universities .
The main steps that are performed during a chemical analysis are the following: (1) sampling, (2) field sample pretreatment, (3) laboratory treatment, (4) laboratory assay, (5) calculations, and (6) results presentation. Each must be executed correctly in . Definition: An assay is a laboratory technique used to measure, analyze, or detect the presence, quantity, or activity of a substance within a sample. Types: Assays come in various forms, including biochemical, immunoassays, cell-based, molecular, chemical, microbiological, radiometric, and more. Applications: Assays are employed in diverse fields . Automation is a key feature of biochemical analyzers, enabling high-throughput analysis and improving laboratory efficiency. These instruments can process a large number of samples in a relatively short time, significantly reducing turnaround times and increasing productivity. . What Are The Different Types Of Biochemical Analyzer?Types of clinical laboratory analyzers. A clinical laboratory is an institution equipped with the necessary means to carry out analyzes that contribute to the study, prevention, diagnosis and treatment of health problems. Thanks to technological advances, clinical laboratories have incorporated in their different areas (biochemistry, hematology .
Biochemistry analyzers also known as clinical chemistry analyzers are essential laboratory instruments utilized for the quantitative analysis of biochemical substances in biological samples. These analyzers play a critical role in diagnosing diseases, monitoring patient health, and guiding treatment decisions with precise and reliable results.
A urinalysis is a set of tests on your pee (urine). You provide a urine sample, either in a cup or with a catheter. Then your provider sends it to a lab for a visual exam, dipstick test and microscopic exam. You might need a urinalysis as part of a routine screening or if you have symptoms of an infection, diabetes, or kidney or liver issues. Types of mercury analyzer. Mercury analyzers are used to detect mercury levels in solids, liquids, or gases for environmental and safety reasons. Analysis may be carried out on a per-sample basis or for continuous .Hematology analyzers are used widely in patient and research settings to count and characterize blood cells for disease detection and monitoring. Basic analyzers return a complete blood count (CBC) with a three-part differential . Types Of Soil Tests. The analysis type depends on the explored components or properties of the field ground that may beneficially or adversely impact crop development. The most frequently-used types analyze and measure: . Send samples for a professional analysis to a state or private laboratory. Soil test procedures in some local labs are free.
Laboratory medicine service in a hospital is concerned with relevant investigations of patient’s presenting complaints and sometimes with detection and potential prevention of disease. It involves a systematic approach of clinical advice or request for a particular investigation, analysis of the collected specimen, interpretation of results, and .Laboratory-based X-ray fluorescence analyzers (XRF analyzers) are used in process control and analytical labs for a wide range of applications across industries . Meet demanding materials analysis requirements with qualitative and quantitative characterization of all types of conductive and non-conductive unknown samples. .What Are the Different Types of Laboratory Tests? Clinical chemistry uses chemical processes to measure levels of chemical components in body fluids and tissues. The most common specimens used in clinical chemistry are blood and urine. Many different tests exist to detect and measure almost any type of chemical component in blood or urine.
Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to separate, identify, and quantify matter. [1] In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separation isolates analytes. Qualitative analysis identifies analytes, while quantitative analysis determines the numerical amount or .Hematology analyzers (also spelled haematology analysers in British English) are used to count and identify blood cells at high speed with accuracy. [1] [2] [3] During the 1950s, laboratory technicians counted each individual blood cell underneath a microscope.Tedious and inconsistent, this was replaced with the first, very basic hematology analyzer, engineered by .
Types of Chemistry Analyzers: A Compr
Selecting the right analyzer technology to meet your
Image 9: This is how a mercury analyzer in a laboratory setting looks like. Picture Source: encrypted-tbn0.gstatic.com What are the different types of spectrophotometer? Visible light spectrophotometer – This type of spectrophotometer uses a visible light from a tungsten lamp. It is typically used for routine laboratory work, specifically the portable and bench-top .
We understand the importance of compliance and accuracy in laboratory analysis, which is why our analyzers are designed to adhere to strict quality standards. . Types of Analyzers Your Laboratory may need. HbA1c Analyzer. The HbA1c Analyzer YR05129 is an advanced and compact device designed to measure HbA1c levels in whole blood samples. This . 1. Introduction One of the most important properties of the soil is the grain properties. The grain properties of soils are the particle size, grain shape and mineralogical composition. Thus, to determine the particle or grain size of such soil, a procedure commonly referred to as sieve analysis is done. Determination of the [.] Medical laboratory jobs are positions in medical and clinical environments in which individuals perform testing, research, analysis and reporting for health care and medical processes. Medical laboratory employees conduct tests on clinical specimens to collect information about a patient or otherwise aid in the testing processes that lead to .
why is my moisture meter not working
Divirta-se com os nossos sorteios e concorra a prêmios incríveis! Sorteios a cada 5 min, somando mais de 500 mil em prêmios por dia! São 50 prêmios acima de 1 mil, e você descobre o resultado na hora! São 700 prêmios acima de 2 mil, e você descobre o resultado na hora! 5 sorteios durante a semana de até R$ 2.500 em prêmios por sorteio.
types of analyzers in laboratory|ARCHITECT c4000 Clinical Chemistry